Exercise and Stem Cells
The future of exercise revolves around leveraging your body’s regenerative potential — from muscle repair to reducing inflammation and optimizing recovery.

When you exercise your bodies natural repair system kicks in with the activation and mobilization of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). This is the process where your body starts to repair microtears and inflammation from your exercise activity. It can help in the support of muscle regeneration, enhance bone density and strength and reduces exercise systemic inflammation by releasing anti-inflammatory factors.
While many people focus on protein in their post-workout meals, there’s emerging evidence suggesting that certain dietary strategies can enhance MSC activation, amplifying the regenerative effects of exercise. By making simple nutritional adjustments before and after your workout, you might significantly increase stem cell production and speed up recovery.
Exercise alone triggers a controlled stress response that primes stem cells for repair. When combined with the right nutrition, the effects can be magnified. And It doesn’t have to be complicated or time-consuming to incorporate these small changes. Even something as simple as enjoying a couple of squares of dark chocolate after training, or marinating your chicken breast in olive oil, pepper, and turmeric, can make a significant difference in supporting your body’s ability to generate more stem cells.
- Pre-workout – nutrients and fasting strategies may enhance stem cell sensitivity and readiness
- Post-workout – specific foods and compounds can fuel MSC proliferation and tissue repair
- Anti-inflammatory nutrients – like polyphenols, omega-3s, and sprout-based foods may help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, supporting regenerative potential
Foods that influence stem cell generation
- Broccoli sprouts – contain sulforaphane, which activates detox pathways and supports stem cell health.
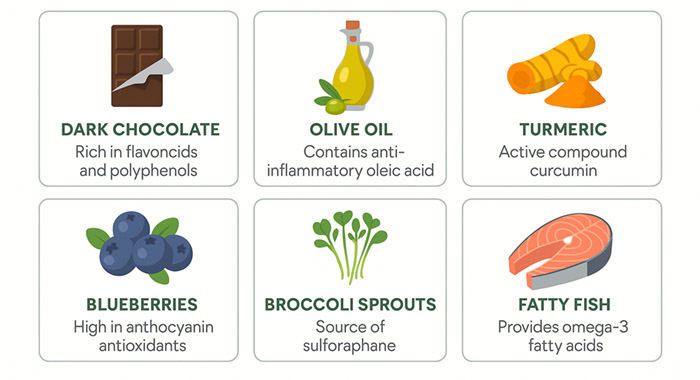
- Dark chocolate – rich in flavonoids and polyphenols, reducing oxidative stress and supporting vascular health.
- Green tea – rich in EGCG, a polyphenol known to support stem cell function and reduce oxidative stress.
- Olive oil – contains anti-inflammatory oleic acid, improving stem cell signaling.
- Turmeric – active compound curcumin enhances stem cell proliferation and reduces inflammation.
- Blueberries – high in anthocyanin antioxidants, protecting stem cells from oxidative damage.
- Fatty fish – provides omega-3 fatty acids that reduce inflammation and support regenerative capacity.
Foods that support Stem Cells
🌿 Stem Cell–Rich Pre-Workout Meal
Below is just two quick sample meal for before and after exercise demonstrating how easy it is to incorporate stem cell rich foods into the diet.
- Green tea (hot or iced) – packed with EGCG, an antioxidant that supports stem cell activation and reduces oxidative stress.
- Greek yogurt with blueberries – provides probiotics and anthocyanins to nourish gut health and deliver anti-inflammatory effects.
- Sprouted grain toast with avocado & olive oil – combines whole grains, healthy fats (including oleic acid), and fiber to stabilize blood sugar and reduce systemic inflammation.
**A sprinkle of turmeric and black pepper to the avocado mash for curcumin absorption. Curcumin is fat-soluble and needs to be dissolved in fat to be absorbed by the body. When black pepper is combined with curcumin, it has been shown to increase bioavailability by 2000%
🌿 Stem Cell–Rich Post-Workout Meal
- Grilled salmon or mackerel – rich in omega-3 fatty acids to reduce inflammation and support regenerative capacity.
- Steamed broccoli sprouts – high in sulforaphane, which activates detox pathways and promotes stem cell health.
- Turmeric-spiced vegetable and chicken stir-fry – delivers curcumin and phytonutrients to reduce post-exercise inflammation.
- Green tea – aids recovery with EGCG’s antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits.
- 2 Squares of 90% Dark Chocolate – provides flavonoids and polyphenols, which help reduce oxidative stress and support healthy blood vessels, creating a more supportive environment for stem cells.
Learn More from Trusted Sources
- Cell Metabolism – Dietary Interventions to Improve Metabolic Health
- National Library of Medicine – The Role of Mitochondria in Metabolic Health
- Cardiometabolic health improvements upon dietary intervention are driven by tissue-specific insulin resistance phenotype: A precision nutrition trial
- PUB MED! Intermittent Fasting and Metabolic Health
StemCell Regen Newsletter
Sign up for our newsletter and receive a free Ebook

